A look at how GraphDB 11.1’s chatbot tool helps you quickly setup and evaluate Graph RAG using different LLMs
Using Talk to Your Graph (TTYG) in GraphDB 11.1 is more flexible and versatile than ever with extended support for a variety of LLM providers. Previously, all AI features were based on the OpenAI Assistant API and it was impossible to use any other models not compliant with this API. Starting from GraphDB 11.1, the scope of supported providers has been greatly increased, including support for locally hosted solutions. Having the flexibility to choose your model addresses several issues:
- Privacy concerns: Some users are reluctant to send data to third-party APIs due to compliance requirements, intellectual property risks, or confidentiality policies.
- Cost considerations: OpenAI’s usage-based pricing can become expensive for large-scale or high-frequency queries. Other providers or self-hosted models might offer cheaper or more predictable alternatives.
- Flexibility and innovation: Supporting multiple providers, including open-source LLMs, fosters a more dynamic AI ecosystem. This also opens up opportunities to integrate with cutting-edge LLM solutions or custom user-trained models.
How to configure LLM use in GraphDB 11.1
You can configure the LLM you want to use in GraphDB 11.1 by providing the following properties. You can find a full reference of these properties and the values they can take in the documentation.
graphdb.llm.api– This property controls which API provider GraphDB will be using, and can take one of the following values:openai-assistantsopenai-completionsopenai-completions-http1.1geminigraphdb.llm.api-keygraphdb.llm.urlgraphdb.llm.model
openai-completions vs openai-completions-http1.1
Some LLM software (such as LMStudio and vLLM) requires an HTTP 1.1 client. For this reason, GraphDB 11.1 allows you to choose between the regular openai-completions API, and the openai-completions-http1.1. The table below illustrates the necessary configurations for some of the currently popular LLMs we have tested.
| LLM | graphdb.llm.api | graphdb.llm.url | graphdb.llm.api-key | graphdb.llm.model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenAI Completions API | openai-completions | Not required, points to OpenAI by default | <your Open AI API key> | Any OpenAI model https://platform.openai.com/docs/models |
| LMStudio | openai-completions-http1.1 | <your LMStudio API URL/>, for examplehttp://127.0.0.1:1234/v1 | “none”, since LMStudio does not require an API Key | The model you setup in LMStudio, one of https://lmstudio.ai/models |
| vLLM | openai-completions-http1.1 | <your vLLM API URL/>, for example http://127.0.0.1:1234/v1 | “none”, since LMStudio does not require an API Key | The model you setup in vLLM https://docs.vllm.ai/en/v0.9.2/models/supported_models.html#download-a-model |
| DeepSeek | openai-completions | https://api.deepseek.com/v1 | <your Deepseek API key> | deepseek-chat |
| Databricks | openai-completions | https://dbc-xxxxxxx.cloud.databricks.com/serving-endpoints/ | <your Databricks API key> | <the model you have in Databricks> |
| Gemini | gemini | Not applicable, always points to gemini | <your Gemini API key> | https://ai.google.dev/gemini-api/docs/models |
| Gemini OpenAI | openai-completions | https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/openai/ | <your Gemini API key> | https://ai.google.dev/gemini-api/docs/models |
| Azure OpenAI | openai-completions | https://xxxxxxx-graphdb2.openai.azure.com/ | <your Azure API key> | https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/ai-foundry/openai/concepts/models?tabs=global-standard%2Cstandard-chat-completions |
Any other LLM provider can be set up if it exposes the OpenAI Completions REST API by using the openai-completions value for the graphdb.llm.api property and the URL of the API for the graphdb.llm.url property. Let’s talk to our graph using a locally hosted model with LMStudio.
Talk to you graph with the Qwen3-32B model
Configure the model in LMStudio
For this example we are using a server with NVIDIA RTX 6000 with 48G VRAM. On the server we have started LMStudio and have loaded the Qwen3-32B-Q4_K_M version of the model with the cli of LMStudio. We have loaded the model with the following context window size:
lms load qwen3-32b --context-length 32768
Why this model?
We need a model that is capable of function calling. Qwen is also good at SPARQL query generation and has a good context window size. Required context window size depends on the size of the ontology. Models need the ontology to generate SPARQL queries and GraphDB sends the ontology to the LLM with each prompt. GraphDB also keeps the memory of the messages and sends some of them to the LLM, which also increases the prompt. GraphDB estimates whether the prompt will fit the context limit and once the prompt is close to reaching it, GraphDB will try to remove some messages from memory, which may lead to some unexpected behaviour.
To verify that you can access the model from GraphDB, execute the following curl command, where http://x.x.x.x:1234 is the LMStudio server location.
curl http://x.x.x.x:1234/v1/models
{
"data": [
{
"id": "qwen3-32b",
"object": "model”,a
"owned_by": "organization_owner"
}
],
"object": "list"
}%
Note that GraphDB “tells” the model how to “talk to it” using the configured query methods but cannot guarantee that the model will succeed in doing so. In general, the rule is the bigger the model and the context window, the better results it will produce.
Configure GraphDB to use the model
- Download GraphDB 11.1. For this example we are using the GraphDB 11.1 distribution.
- Go to GraphDB bin directory (by default it should be graphdb-11.1/bin) and start GraphDB in the following way (full reference on GraphDB configuration you can find here.):
./graphdb -Dgraphdb.llm.api=openai-completions-http1.1 -Dgraphdb.llm.url=http://x.x.x.x:1234/v1 -Dgraphdb.llm.api-key=none -Dgraphdb.llm.model=qwen3-32b
- Setup your GraphDB license
Now let’s talk to your graph!
GraphDB documentation described well how to use the Talk to you Graph feature. We will use the sample datasets from the documentation to demonstrate the feature with some small changes in the agent configuration.
- Follow the documentation to create the Star Wars repository.
- Go to Lab -> Talk to Your Graph.
- Create an agent the way it is explained in the documentation with the following changes:
- Configure the model context window to 30,000.
- We advise setting the temperature to 0 to improve accuracy and make the model’s output deterministic.
- Check the Auto-add missing namespaces to avoid errors when the generated queries are missing the necessary namespaces.
- Set the maximum results of the FTS query method to 10 or similar. This is very important, since the FTS query, by default, returns a lot of results, which are then sent to the model and this fills the context window quite quickly, leading to unnecessary behaviour. You can also reconfigure the tools’ queries if you need to customize further Talk to You Graph.
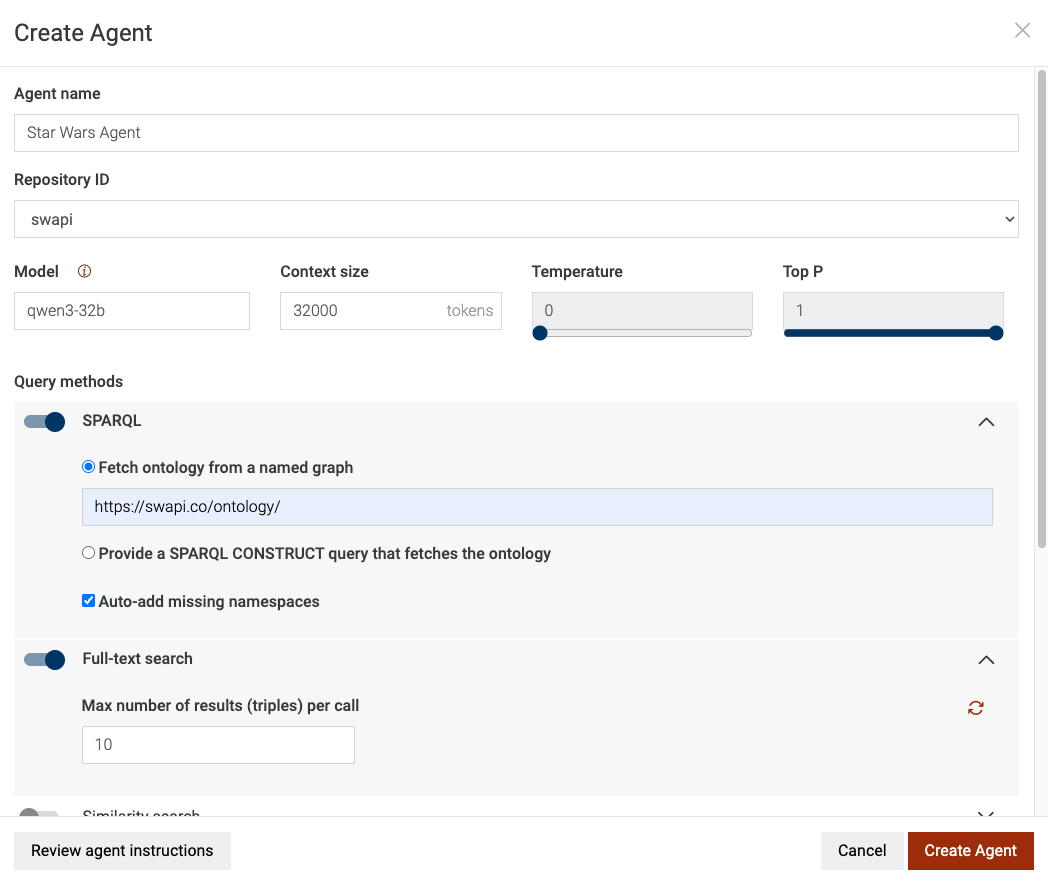
Your agent configuration should look like this:
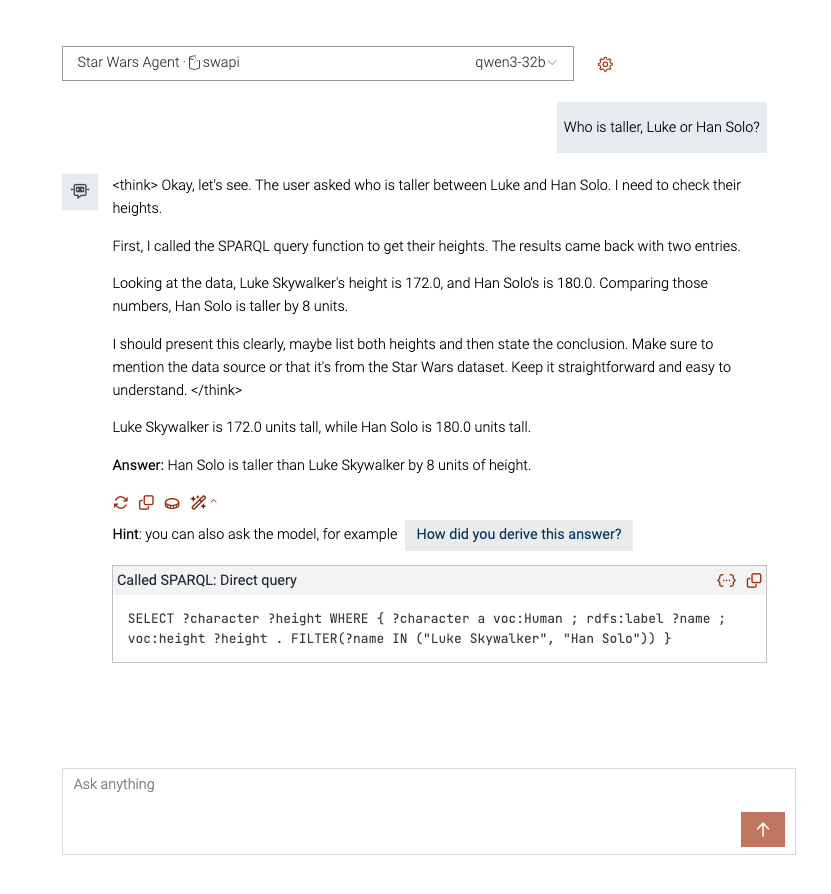
And let’s ask some questions:
- “Who is taller, Luke or Han Solo?”. Click on the magic wand to find out how TTYG derived the answer.
- “Where is Han Solo from?” Click on the magic wand to find out the SPARQL queries the model wrote to find the answer from GraphDB.
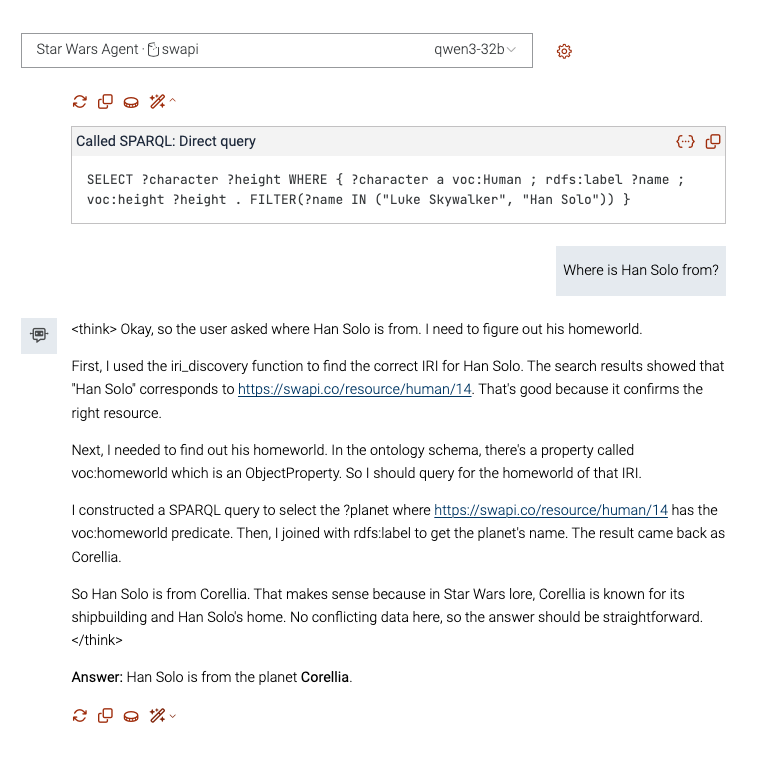
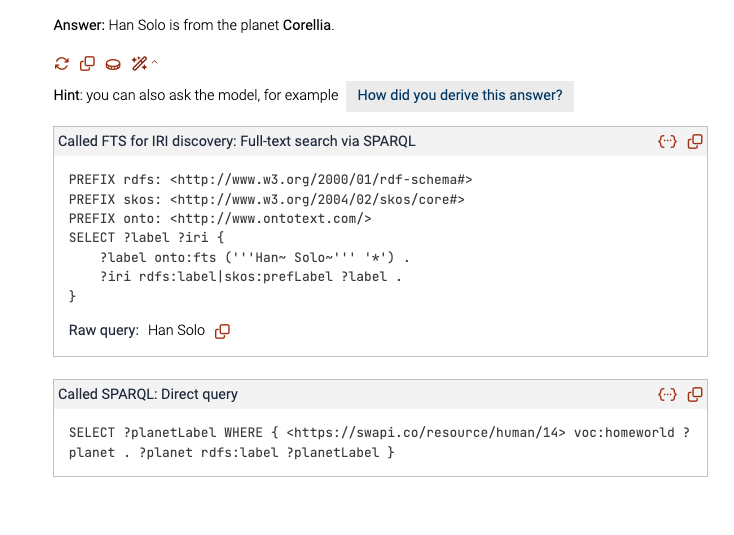
So the model is pretty descriptive and along with the answer you get an explanation on how it was derived. It is also good to check the magic wand to see actually how the model succeeded to “talk to your graph” via SPARQL queries.
If you are curious what happens behind the scenes, you can see the full HTTP requests that GraphDB sends to the LLM API in the GraphDB logs. You need to start GraphDB in debug mode by adding the following property: -Dgraphdb.logger.root.level=DEBUG
GraphDB’s documentation provides more thorough explanations of TTYG and the Query methods (or tools) that can be exposed to the LLMs.
GPT functions and explain
Once you configure the LLM for GraphDB, you can also use the other AI features such as the GPT SPARQL function and explain. The same model will be used by default, but you can still reconfigure the model of these features with the graphdb.gpt-sparql.model property.
To wrap it up
The TTYG chatbot tool of GraphDB 11.1 helps you quickly setup and evaluate Graph RAG using different LLMs. If you want to integrate GraphDB in your Graph RAG solution you can use all GraphDB query methods through the MCP protocol or through a REST API. This has never been easier with GraphDB 11.1. You can find out more in the documentation.
Ready to explore the TTYG tool with any LLM?

